Introduction
The Cannabis Sativa plant, more commonly known as marijuana, is a complex organism with a variety of components, each playing a crucial role in its growth, development, and overall functionality. This article delves into the intricate anatomy of a marijuana plant, exploring the functions, characteristics, and significance of its root system, stem, leaves, flowers, and other integral parts.
So let’s get to know this incredible plant a little better and understand more on each of its parts and what they do.
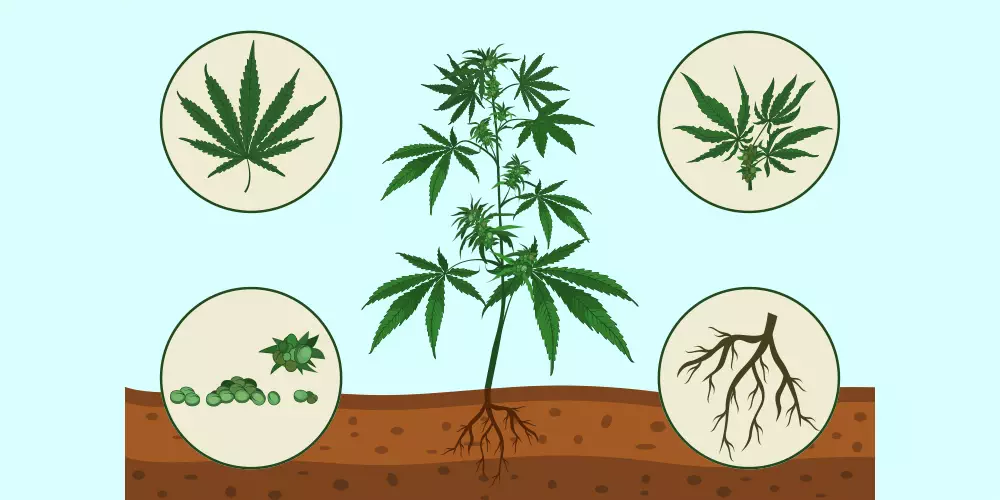
Root System & Stem
Just with any plant the root system of a marijuana plant is crucial as it performs the pivotal role of absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. While the stem acts as the plant’s backbone, providing support to keep it upright and serving as the transportation hub for nutrients, water, and sugars between the roots and the rest of the plant.
Leaves
Marijuana plants possess very distinct leaves, you will have seen them adorned on an endless amount of things, usually characterized by their serrated edges and palmate structure. The leaves are the site of photosynthesis, a process where light energy is converted to chemical energy, fueling the plant’s growth and development. They are crucial for the plant’s energy production and overall health.
Types of Leaves
- Fan Leaves
- Appearance: These are the large, protruding leaves that are most iconic and easily recognizable as being from a cannabis plant. They usually have serrated edges and are palmately (look like an open hand), typically with 5 to 9 leaflets.
- Function: Fan leaves play a crucial role in the plant’s photosynthesis process, absorbing light and converting it to energy to support the plant’s growth and development. While they contain lower levels of cannabinoids compared to other plant parts, they are vital for the plant’s overall health and vigor.
- Sugar Leaves
- Appearance: Sugar leaves are smaller leaves that grow within the buds or colas of the marijuana plant. They are called sugar leaves due to the high concentration of trichomes on their surface, giving them a sugary, crystalline appearance.
- Function: Sugar leaves are important because they are rich in cannabinoids and terpenes. They are often used in the production of concentrates, edibles, and other marijuana products due to their potency.
Flowers
Flowers are the reproductive organs of the plant. They are distinguished by their sex; male flowers produce pollen, while female flowers produce seeds when pollinated. The female flowers are significant to marijuana users as they contain higher concentrations of cannabinoids, the compounds responsible for the plant’s effects. The flowers are the sought-after component for both recreational and medical users due to their potency and range of effects.
Types of Flowers
1. Male Flowers
Male flowers are typically smaller and less conspicuous compared to their female counterparts. They develop in clusters and produce pollen, which is necessary for fertilizing female flowers. Male flowers are generally not consumed as they contain lower levels of cannabinoids, the compounds responsible for the effects of marijuana.
2. Female Flowers
Female flowers, often referred to as buds, are the primary focus for marijuana consumers. They are typically larger and more resinous than male flowers.
When unpollinated, female flowers focus on producing cannabinoids and terpenes, resulting in higher potency. If they are pollinated by male flowers, they will produce seeds and will have lower cannabinoid content.
3. Hermaphroditic Flowers
Some marijuana plants can develop both male and female flowers, a condition known as hermaphroditism. This usually occurs due to environmental stress or genetic instability. Hermaphroditic plants can self-pollinate, which is generally undesirable for growers focusing on producing seedless, high-potency buds.
4. Sinsemilla
The term “Sinsemilla” refers to female marijuana plants that have not been pollinated and, thus, do not produce seeds. Sinsemilla buds are often more desirable due to their higher cannabinoid and terpene concentrations, providing more pronounced effects and flavors compared to seeded buds.
Parts of the Flowers
1. Pistil
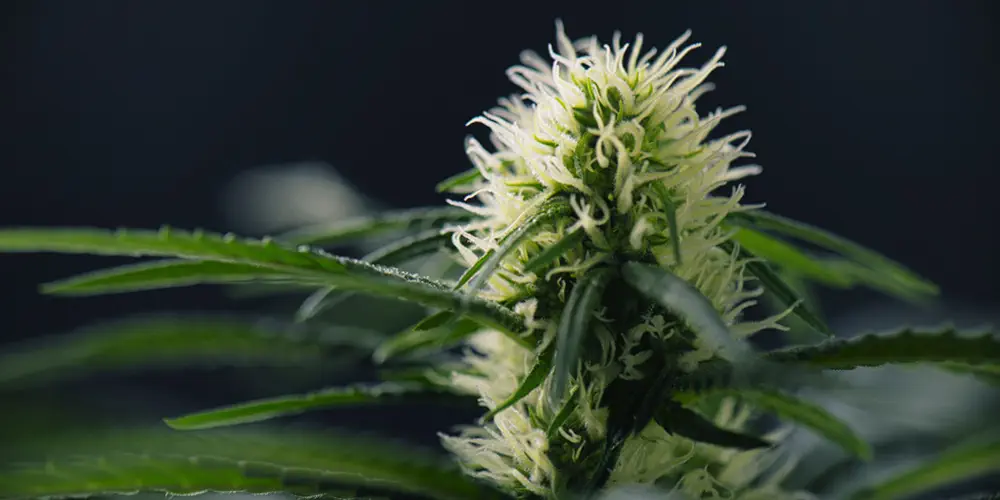

The pistil is the female reproductive organ of a flower. In marijuana, it is easily recognizable as it features colorful, hair-like structures called stigmas, which can be red, orange, or brown, and are responsible for capturing pollen from male flowers.
2. Calyx
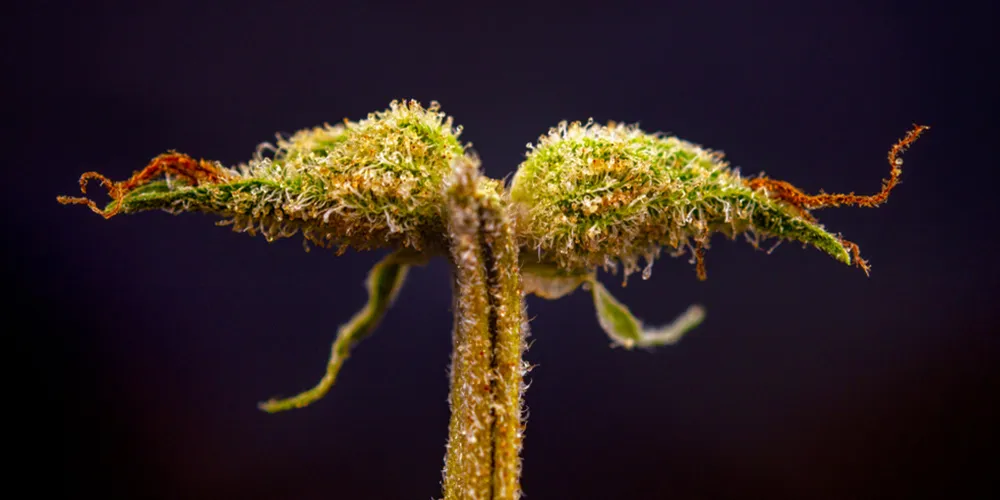

The calyx is the first part of the flower to develop and consists of small, leaf-like structures called sepals, which protect the developing flower bud. The calyx plays a crucial role in supporting and housing the plant’s reproductive organs. In female plants, it can also hold the trichomes, which produce cannabinoids and terpenes.
3. Trichomes
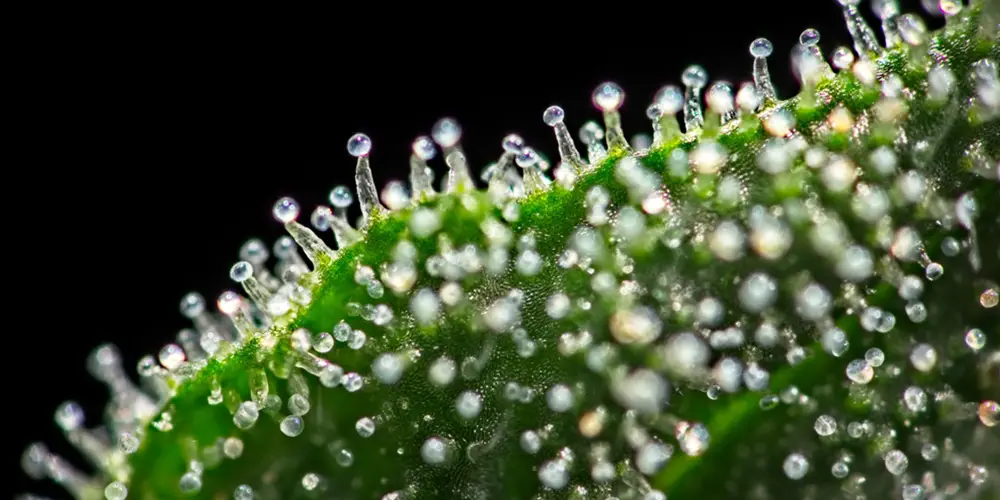

These are tiny, crystalline structures present on the surface of the buds and leaves. Trichomes produce and store the cannabinoids (like THC and CBD) and terpenes that give marijuana its effects and flavors.
4. Cola
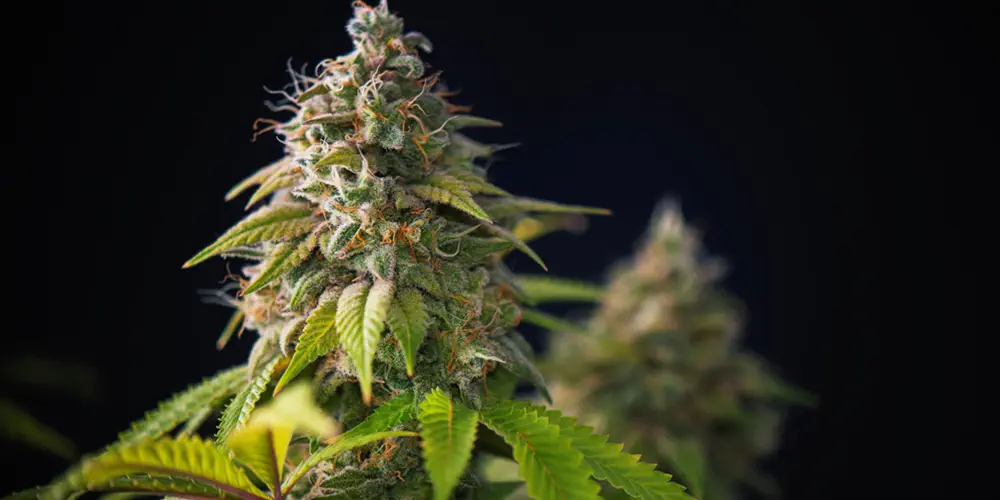

The cola refers to the clustered arrangement of buds on a branch. The main cola, also known as the apical bud, forms at the top of the plant, while smaller colas form along the lower branches.
5. Bract and Subtending Leaf
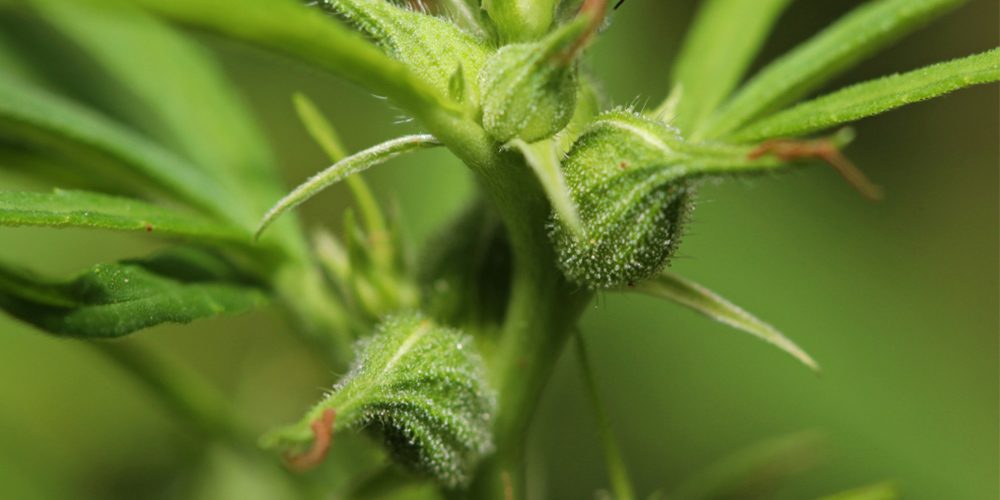

The bract is a small, leaf-like structure that envelops the female flower’s reproductive parts. It is generally coated with resin-secreting trichomes. The subtending leaf, a small leaf that grows at the base of the bract, is also usually covered in trichomes.
6. Stamen
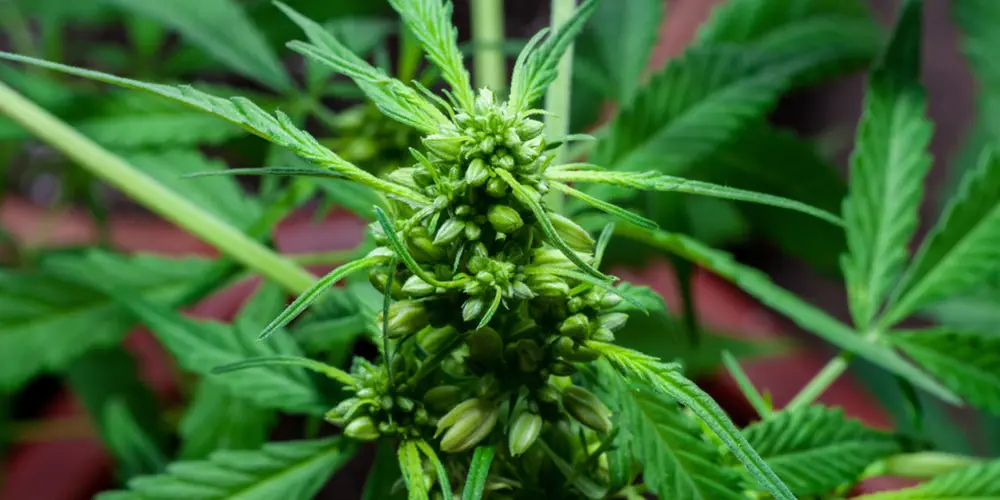

The stamen is the male reproductive organ of a flower and is found in male marijuana flowers. It consists of a filament and an anther, which produces and releases pollen to fertilize female flowers.
7. Seed
If a female flower is pollinated by a male, a seed will develop within the bract. Seeds can be used to grow new marijuana plants.

Cannabinoids and Terpenes
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds synthesized by the marijuana plant, with THC and CBD being the most well-known. They interact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system to produce various effects, ranging from psychoactive to therapeutic. Terpenes are aromatic compounds that determine the scent and flavor profile of the plant. Both cannabinoids and terpenes are vital for medical and recreational use due to their synergistic interactions and varied effects.
Life Cycle of a Marijuana Plant
The life cycle of a marijuana plant encompasses several stages, starting from seedling and progressing through vegetative growth, flowering, and finally, seed production. Each stage requires specific care and environmental conditions to ensure healthy development and optimum yield.
Importance of Each Part
Each part of the marijuana plant contributes uniquely to its growth, development, and potency. The integrated functioning of roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and trichomes ensures the plant can thrive, reproduce, and produce the essential compounds that are valuable to users.
Cultivation Tips
Understanding the function and importance of each part of the marijuana plant is crucial for successful cultivation. Proper care of each component, from root to flower, can lead to healthier plants, higher yields, and more potent buds. Knowledge of plant anatomy can aid in identifying issues, optimizing care, and maximizing the plant’s potential.
Conclusion
From the foundational roots and supportive stem to the energy-transforming leaves and reproductive flowers, each part is essential in creating the resilient and multifunctional marijuana plant.
Furthermore, understanding the roles and importance of each part is pivotal for those involved in the cultivation, with each section needing specific care to ensure the maximum yield and potency.