Male cannabis plants, often overshadowed by their more popular female counterparts, hold untapped potential and serve vital purposes in the world of cannabis cultivation and industry. While females are known for producing the prized buds rich in cannabinoids, males play a crucial role in the process of breeding new strains and contributing to the hemp industry.
Let’s explore the alternative uses of male cannabis plants, from breeding to cannabinoid extraction.
Potency and Cannabinoid Content
In contrast to female cannabis plants, male plants are not sought after for their cannabinoid content or potency. While female plants produce the valuable cannabinoids THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) in abundance, male plants produce significantly lower quantities of these compounds.
Male plants typically contain trace amounts of THC and CBD, but the levels are insufficient for any practical use or consumption.

Why Are Male Plants Not Desired?
Aside from their low THC and CBD content, another key factor that male plants are removed from growing operations is their potential to pollinate female plants. If male plants are present, they will produce pollen that can be carried by the wind or insects to nearby female plants. When female plants are pollinated, they shift their energy from producing high-quality buds to developing seeds. As a result, the potency and overall quality of the buds are significantly reduced. Moreover, the presence of seeds in the flowers negatively impacts their market value and appeal to consumers, making seedless (sinsemilla) buds highly preferred in both recreational and medicinal markets.
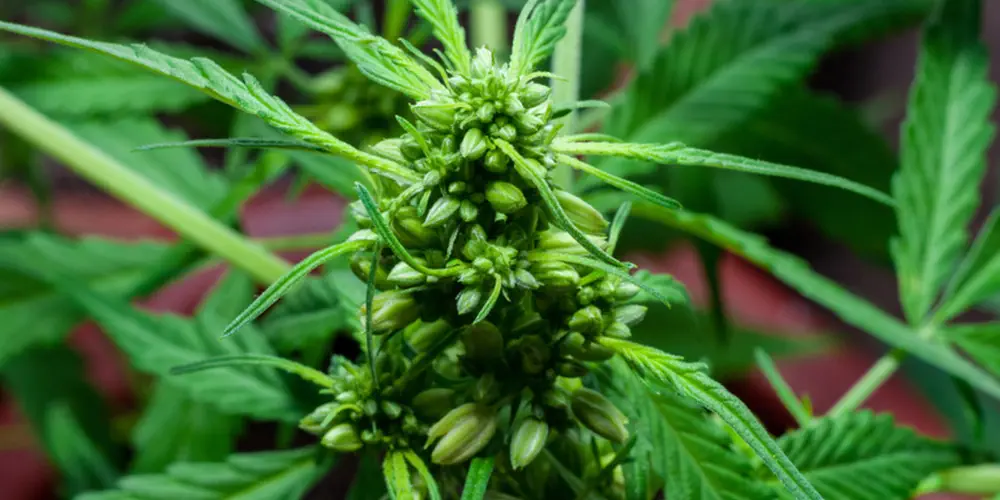

Characteristics of Male Weed Plants:
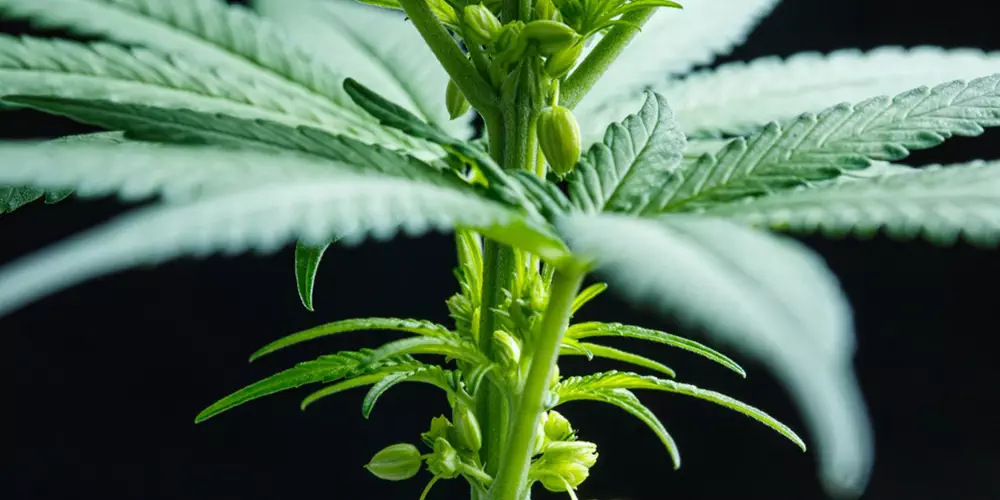
Male weed plants exhibit distinct physical characteristics throughout their life cycle. During the early vegetative stage, they may appear similar to female plants, with thin, elongated stems and serrated leaves. However, as they mature, several differentiating features become evident:
- Pre-Flowering Stage: Male plants start to reveal their sex during the pre-flowering stage, typically occurring around 4-6 weeks after germination. At this point, small clusters of pollen sacs, also known as pollen sac clusters, form at the nodes where leaves and branches meet. These sacs are oval-shaped and have a soft, pod-like appearance.
- Flowering Stage: As male plants enter the flowering stage, the pollen sacs develop further and become more prominent. They will gradually swell and change color, usually from green to yellow or brown, as they approach maturity. Unlike female cannabis plants, male plants do not produce pistils (female reproductive structures) at their nodes.
By closely observing node structure, pre-flowers, and flowering clusters, growers can effectively manage their crops, control breeding, and produce high-quality, seedless cannabis flowers.

Uses of Male Cannabis Plants
Although in general they are not desired by cannabis growers, it does not mean that male plants have an important part to play in the overall cannabis industry. Let’s explore how these plants are used.
Breeding New Strains
Male cannabis plants are indispensable contributors to the world of cannabis breeding. Breeders selectively pair desirable male and female plants, aiming to combine specific traits and characteristics from each parent into a new strain. The male’s genetic material, delivered through pollen, plays a significant role in influencing the offspring’s growth patterns, cannabinoid profiles, and overall health. By carefully crossbreeding various males and females, breeders can create novel strains with unique flavors, aromas, and effects, catering to diverse preferences and market demands.
Industrial Hemp Production
Beyond recreational or medicinal use, male cannabis plants find purpose in the industrial hemp sector. Hemp is a versatile crop with numerous applications, ranging from textiles and construction materials to biofuels and food products. Male hemp plants are valued for their fibrous and thicker stalks, which are rich in cellulose and used in the production of paper, rope, and textiles. Additionally, hemp seeds derived from male plants are a valuable source of nutritious oils and protein-rich food products.
Research and Development
Male cannabis plants also play a vital role in scientific research and development. Understanding the genetic traits and characteristics of male plants can lead to valuable insights into cannabis biology and its potential applications. Researchers use male plants to study various aspects of plant genetics, reproductive biology, and cannabinoid synthesis. Such research can help improve cultivation practices, enhance crop yield, and contribute to the development of more effective medicinal cannabis products.
Sustainable Cultivation Practices
Integrating male cannabis plants into cultivation practices can promote sustainability within the cannabis industry. By utilizing males for breeding purposes and hemp production, growers can diversify their operations, reducing reliance on single-use, high-THC female plants. A more diverse cannabis cultivation approach contributes to the preservation of genetic biodiversity and ensures the long-term viability of the industry.

To Sum Up
Male cannabis plants are not mere bystanders in the world of cannabis cultivation. They offer a range of alternative uses as we have outlined. For growers, accurate identification of male and female weed plants early in the vegetative stage is a fundamental skill for successful cannabis cultivation.