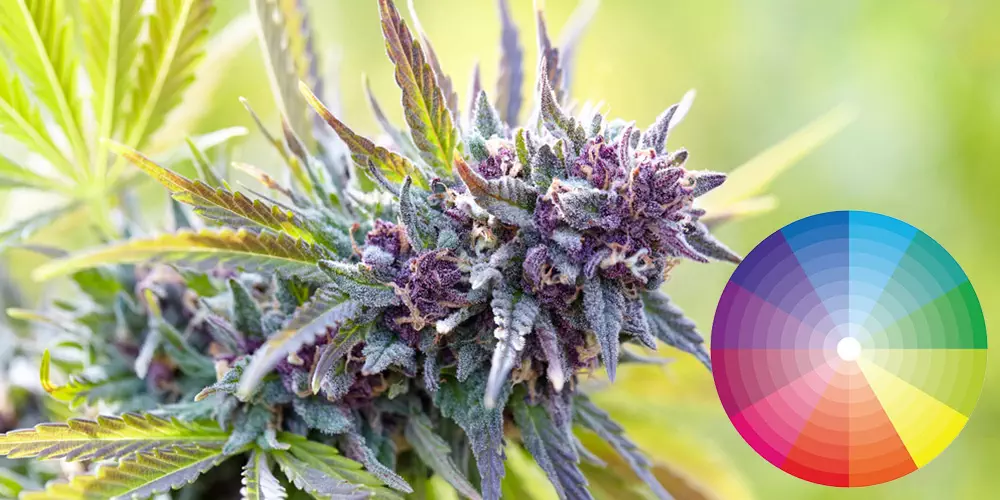
In the world of cannabis, the colors displayed by the plants go beyond aesthetics.
They offer crucial insights into the health, genetics, and environmental conditions that influence their growth.
From the vibrant greens attributed to chlorophyll to the purples, blues, and reds that emerge as plants respond to their surroundings, each hue tells a unique story about the cannabis plant’s journey. This article delves into the diverse palette of colors found in cannabis and what they signify, highlighting the significance of coloration in understanding the plant’s well-being and potential.
Common Weed Colors
Green
The most common color in cannabis plants is green, attributed to the presence of chlorophyll, a crucial pigment for photosynthesis.
Vibrant green leaves typically indicate healthy growth and proper nutrient uptake.
However, different shades of green can signify specific conditions. Dark green leaves might suggest an excess of nitrogen, while light green could indicate a nitrogen deficiency. Observing the depth of green helps growers fine-tune nutrient levels for optimal plant health.
Purple and Blue

Purple or blue hues in cannabis plants result from anthocyanin pigments, triggered by cooler temperatures during the flowering stage. These colors can provide insights into the plant’s genetics and response to its environment.
While not directly tied to potency, strains with vibrant purple or blue coloring are often considered visually appealing and are sought after by consumers for their unique appearance.
Red and Pink
Occasionally, cannabis plants develop red or pink pigmentation, primarily in pistils and buds. This can result from genetic traits or specific environmental conditions. Some strains naturally produce red or pink pistils, which can be an aesthetic bonus.
However, intense red coloration might indicate stress, which can potentially affect cannabinoid production resulting in a less potent bud.
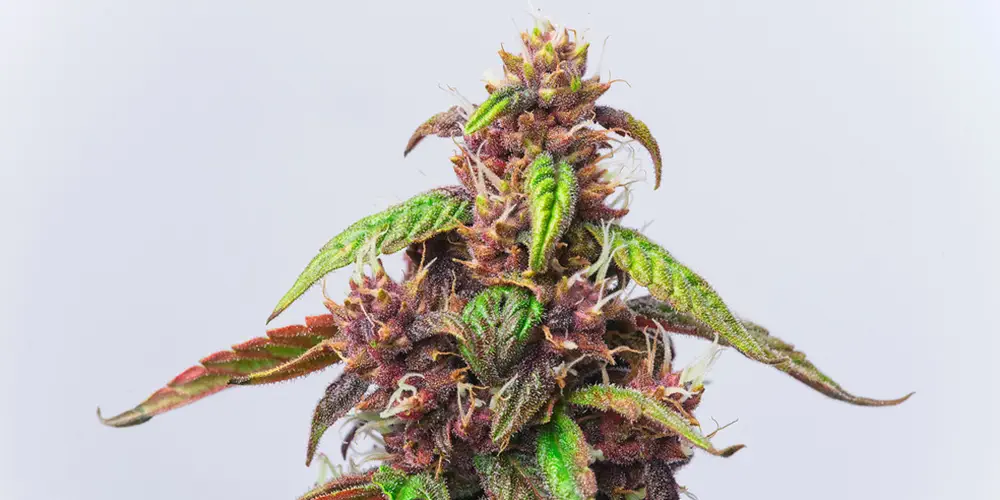

Orange and Brown
As cannabis flowers mature, pistils can transition from white to orange or brown. This change signifies the ripening of the buds.
Orange and brown pistils suggest that the flowers are reaching their peak potency and are ready for harvest.
This color shift is particularly important for growers seeking to harvest cannabis with the desired cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
Yellow
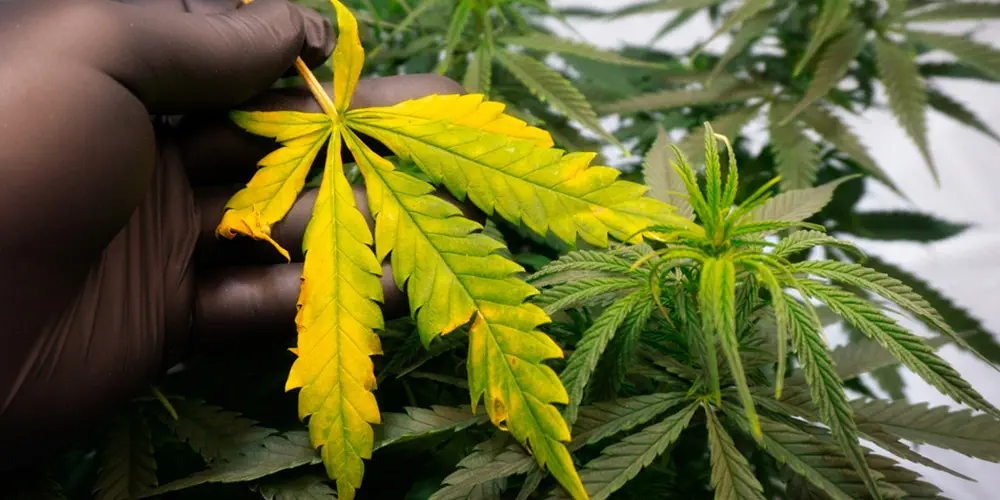

Yellowing leaves can signal various issues.
While older leaves naturally yellow and fall off, widespread yellowing can indicate nutrient deficiencies, light stress, or other problems.
Addressing the underlying cause is crucial to maintain plant health and optimize yield. Monitoring the pattern of yellowing helps growers diagnose and rectify issues promptly.
White and Silver Trichomes
The trichomes, or resin glands, covering cannabis flowers and leaves appear white or silver. Trichomes are the repositories of cannabinoids and terpenes, and their color changes as the plant matures.
Clear trichomes indicate immaturity, while cloudy trichomes suggest the optimal harvest window.
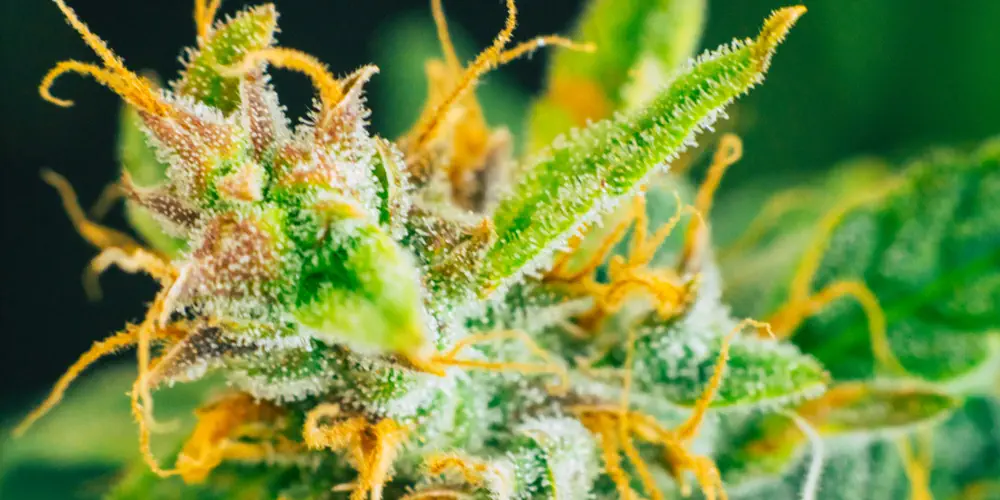

Amber or brown trichomes imply overripeness, resulting in a more sedative effect due to increased cannabinol (CBN) content.
Black Spots
While rare, black spots or areas on cannabis leaves can signal stress, disease, or genetic anomalies. Fungal infections or physical damage can cause black discoloration. Proper hygiene, pest management, and preventive measures are essential to prevent the spread of issues causing black spots.
Multi-Colored Buds
Strains with a diverse array of colors in their buds showcase complexity and genetic diversity. Buds featuring a combination of green, purple, orange, and other hues are often visually striking. These colors reflect the plant’s ability to express various pigments and highlight the interplay between genetics and environment.

How To Increase Bud Colors
Aside from genetic factors and natural variations, there are several cultivation techniques that can be employed to enhance and intensify the colors of cannabis buds. By manipulating environmental conditions and nutrient levels, growers can coax out vibrant hues that captivate the eye and indicate the health and vitality of the plants.
- Temperature Manipulation
- Nutrient Adjustments
- Light Spectrum Manipulation
- Stress Techniques
- pH Management
- Strain Selection
- Harvest Timing
Beyond the techniques mentioned, various environmental factors such as humidity, airflow, and CO2 levels can indirectly influence color development. Providing a stable and controlled environment helps maintain overall plant health and supports the natural processes that contribute to vibrant colors.
Conclusion
The kaleidoscope of colors that cannabis plants exhibit serves as a visual narrative of their life cycle and health. From the lush greens fueled by chlorophyll-driven photosynthesis to the dramatic purples, blues, and reds triggered by temperature and genetics, each shade carries a message. By understanding these colors, growers can decipher the plant’s needs, identify potential issues, and even optimize cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
Moreover, the art of coaxing out and enhancing these colors through cultivation techniques adds another layer of expertise to the journey of cultivating cannabis. As growers harness the power of color, they bridge the gap between science and artistry, cultivating not only healthy plants but also visually captivating and potentially more potent cannabis flowers.